In today’s digital world, we rely on the Domain Name System (DNS) to connect us to websites, applications, and services. Unfortunately, DNS is not as secure as it could be, making it vulnerable to malicious attacks. This is where DNSSEC comes in.
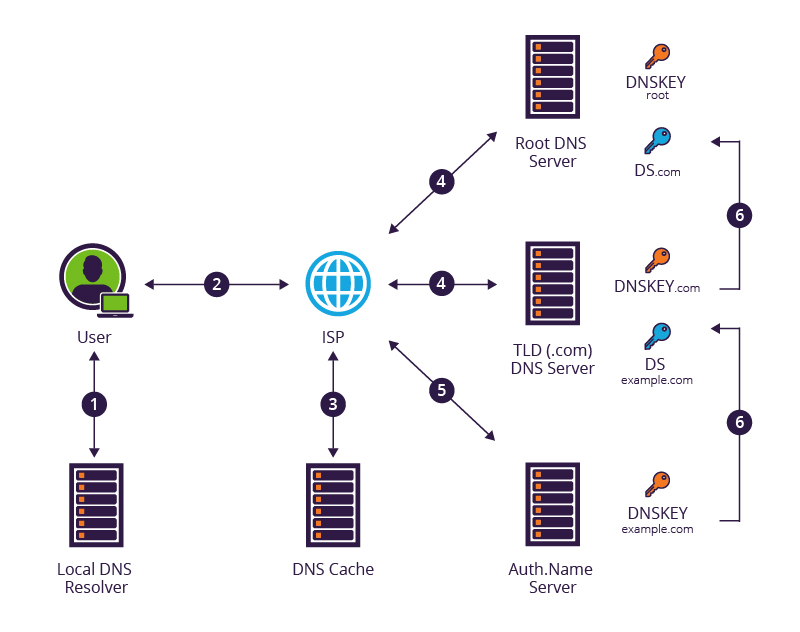
DNSSEC stands for Domain Name System Security Extensions and is an extension of the traditional DNS protocol that adds an extra layer of security. It works by digitally signing DNS records, which in turn allows users to verify the authenticity of the data received from a DNS server. This ensures that the data received is accurate and has not been altered by an attacker.
When DNSSEC is enabled, it prevents DNS spoofing and cache poisoning attacks. DNS spoofing is when an attacker sends false DNS records to a DNS server, causing users to be sent to a malicious website instead of the legitimate one. Cache poisoning is when an attacker sends false DNS records to the DNS server, causing the server to cache the false records and serve them to users even when the legitimate records are requested.
DNSSEC also helps protect users from man-in-the-middle attacks. This type of attack is when an attacker intercepts communication between two parties and alters the data sent. DNSSEC prevents this by digitally signing DNS records, ensuring that the data received is authentic and has not been altered in transit.
DNSSEC is a critical tool for securing the DNS protocol and is an important step in securing the internet. By digitally signing DNS records, DNSSEC ensures the accuracy of the data received, prevents attackers from spoofing or poisoning DNS records, and helps protect users from man-in-the-middle attacks. As organizations become more and more reliant on the internet, DNSSEC is becoming increasingly important and is an essential part of any organization’s security strategy.

No responses yet